New to Java? We'll help you get started with our revised beginner's tutorial, or our free online textbook.
|
|
 Get the latest Java books |
|
|
h t t p : / /w w w . j a v a c o f f e e b r e a k . c
o m /
|
||
|
Menu Articles Using Java Applets Looking for Java resources? Check out the Java Coffee Break directory! |
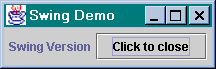
Writing the Swing versionThe code to generate an Swing-based application is actually little different from a purely AWT-based one. The changes between the SwingFrame example, and the AWTFrame example, are highlighted in bold. Figure 4 shows the application in action, with the default 'Metal' L&F. import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class SwingFrame
{
public static void main (String args[])
throws Exception
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Swing Demo");
JLabel label = new JLabel("Swing Version");
JButton button = new JButton ("Click to close");
button.addActionListener( new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
// Get content pane
Container pane = frame.getContentPane();
// Set layout manager
pane.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
// Add to pane
pane.add( label );
pane.add( button );
frame.pack();
// Center the frame
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
// Get the current screen size
Dimension scrnsize = toolkit.getScreenSize();
// Get the frame size
Dimension framesize= frame.getSize();
// Set X,Y location
frame.setLocation ( (int) (scrnsize.getWidth()
- frame.getWidth() ) / 2 ,
(int) (scrnsize.getHeight()
- frame.getHeight()) / 2);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
|
||||
|
|||||